User Tools
Sidebar
Add this page to your book
Remove this page from your book
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Root directories
In order for PMA.core to show content, you need to set up root directories. A root directory is a starting location from which your various whole slide images will be hosted.
The reason for working with root directories offers several advantages:
- You don't have to navigate through a complicated directory structure before reaching the files that you want to work with
- You can map multiple root directories to organize slides according to different purposes or workflows.
- Swtich out different types of storage without the end-user knowing about it. When you move data from a conventional hard disk to cloud, you typically need to install a new piece of software (S3 browser, or an FTP explorer). With PMA.core, you just re-direct the root-directory to point to the updated location and you're done; the end-user remains unaffected
The concept of root directories is not dissimilar to mapped network drives in the Microsoft Windows operating system, where you map a map such as \\myserver\dir\subdir\subsubdir\ to a (much simpler to remember and address) drive letter.
Mounting points
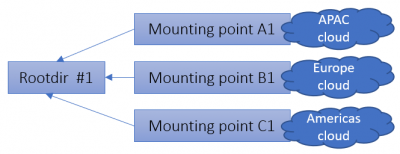
Since PMA.core 2, a root directory is defined by one or more mounting point. This was done to be able to facilitate geo-replication scenarios.
A mouning point for a root directory may either be a local directory, a UNC share, Azure blob storage, FTP folder, or an Amazon S3 compatible storage.
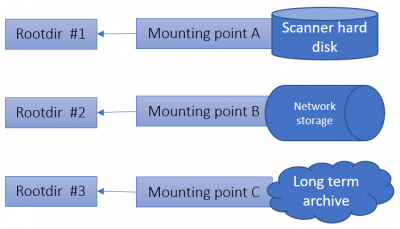
A Mounting point is a further abstraction of the concept “where are my slides stored?”. While most users will end up having one mounting point per any one root directory, here are the different scenarios in which you could have multiple mounting points:
- Automatic failover between different storage types. If a network resource is not available, a fallback could be offered to an alternative location (possibly with a reduced or older dataset)
In order to make root directories work, you need to attach at least one mounting point to it.
The mounting point of a root directory refers to the base directories where the system should look into for whole slide images. All the subdirectories of the root directories are exposed by the application and whole slide images that are discovered are advertised.
Configuration
Root directories management
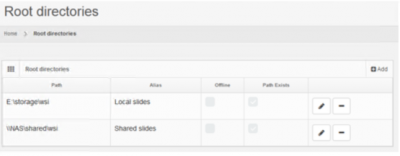
Root directories can be managed by selecting the “Root directories” option under the “Settings” section in the left menu.
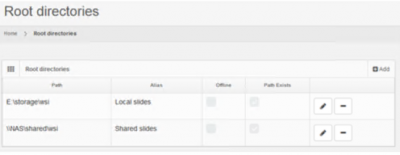
The list displays all the configured root directories and provides options to add new, edit and delete entries.
- The “Offline” column indicates whether or not a root directory is enabled. An offline root directory is not advertised by the system and its contents are not available to the end-users.
- The “Path exists” column indicates whether or not the system is able to mount a root directory's path and access it's contents. For example a root directory that points to a local file system folder, that has been deleted, will not have the “Path exists” column checked.
We have a separate section in this wiki that takes you through the different steps that you can take to configure root directories and mounting points.
Root-directories can be labeled public or private, which allow you to take security precautions when configuring these.
Security
Root directories can be either public or private.
Who's accessed what (either public or private) folder can be monitored via the Access log tab.
Logging
Apart from manipulating root directories, monitoring their use is an important aspect of our software as well.
You can monitor logs for several kinds of acivity:
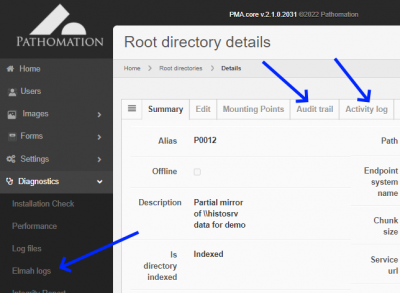
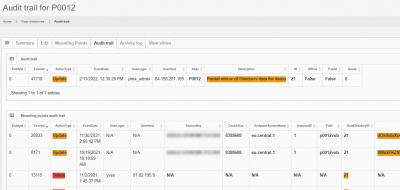
Audit trail
The audit trail tab conbines any operations that were performed on both root directory entries and underlaying mounting point entries.
The presented information 21 CFR pârt 11 compliant.
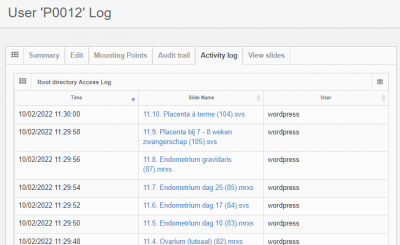
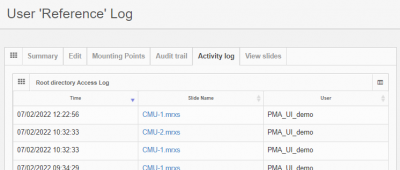
Activity log
In addition to an audit trail, an activity log is available that chronologically tell you which user has been accessing what slides in the root directory:
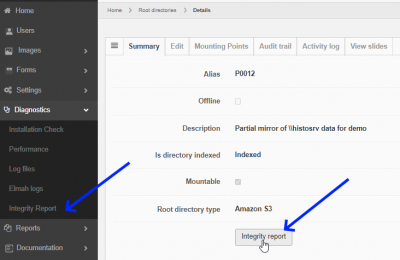
Integrity check
When problems persist over time, a structured and proactive approach is warranted.
When you suspect certain slides in a particular root directory are corrupt, you can run an integrity check on a particular folder:
This attempts to read all slides in a folder and reports on the ones that fail. You should then try to find out why such slides cannot be read.
For problems that only occur occasionally and don't appear to be persistent, Elmah logs are available to assist in for ad-hoc troubleshooting.